Apple basically came up with the MPEG-4 container format MP4 but also came up with the M4B to host audiobooks in AAC format with Artwork and tags of information about the books.
Windows supports M4A format files with basically most of the same functions for storing AAC and Artwork and tags of information, but do not contain the ability to store Chapters or a Bookmark as in an M4B file format.
Within Apple the iTunes program properly handles M4B format and exposes Chapter navigation and stores the last played position as a bookmark.
On Windows the iTunes for Windows program does much the same thing.
However probably the best M4B file format "viewer" or audiobook playback is found with VLC - Video Lan Client 2.2.6 "Umbrella"
In VLC its possible to navigate the chapter marks on the playback timeline as they show up as short vertical grey lines across the bottom of the timeline.
The Playback menu has a complete Chapter menu for jumping specifically to any chapter.
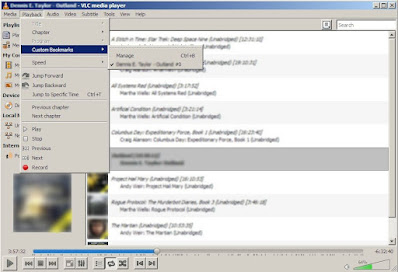
And Custom Bookmarks can be created and written to the M4B file and then referred to so that Playback could jump to a specific Custom Bookmark.
VLC has an xml based Playlist system and a concept for a Media Library that deviates a little from Apple iTunes and Windows Media Player.
First there is the "Media Library" Playlist, disabled by default. It is a special xml playlist stored in the folder with other user interface configuration options;
Example:
C:\Users\jwillis\AppData\Roaming\vlc\ml.xspf
It gets created by turning on the feature under;
Tools> Preferences >"Show Settings - [x] All
Then traveling down to branch [+] Playlist and checking > Use media library
The ml.xspf file gets populated by one of two ways:
1. right clicking with a mouse in the main window and selecting + files or +folders
2. by drag and dropping files or folders on the main window
Then shutting down the VLC client and restarting it will have automatically saved those choices in the ml.xspf file and reload them in the > "Media Library" branch of the [Media Library]
note: VLC will continue to default to loading nothing and focus there on start up, you have to click on the Media Library / Media Library in order to see that it saved your previous media choices.
You can default the Playlist under Media Library / Playlist to refer to a personal xml format .xspf file, but it will not open it.. unless you set the "Default stream" option under:
Tools> Preferences >"Show Settings - [x] All
Then traveling down to branch [+] Playlist and filling out "Default stream [ ________ ]
With a specially formatted "Reverse slash" path prefixed with a file: operator like this -
file:///C:/Users/jwillis/AppData/Roaming/vlc/ml.xspf
And checkboxes that include "Auto start"
But that will also immediately start playing the Playlist.
If you do not it will offer you the choice to open the xspf file to list the choices, but it will not by default display the contents unless clicked upon.
Using the other method with Media Library is frankly closer to what you would expect, you just have to remember to travel to the folder under Playlist to see the most recently saved collection of media.


